|
It was only about 6 years ago that Intel first proposed AGP as a solution to the problems facing visual computing; and since then, both the AGP specification and graphics cards have undergone a number of fundamental changes.
Now, with the introduction of the e-GeForce4 Ti 4600-8X, the fastest graphics interface has been matched with the fastest NVIDIA graphics chip in order to create a powerful new winning combination. The new 8X AGP interface on the e-GeForce4 Ti 4600-8X overcomes problems of the older 4X interface as well as introduces new and powerful features.
Optimizing Graphics Operations and Texture Storage System designs and graphics subsystems in particular have advanced at a rapid pace since AGP 2.0 emerged in 1998. Today, AGP 2.0 and its associated AGP 4X bandwidth has become a bottleneck in the overall flow of graphics-related data.
With
a theoretical bandwidth of 2.1GB/sec., AGP 8X also allows developers to
more efficiently manage scenes with complex geometries, and dynamically
switch to new scenes in real time. By lowering the overhead associated
with storing and Isochronous Operation For Streaming The overall bandwidth improvements of AGP 3.0 benefit all graphics operations involving complex geometries, textures, or streaming. One new AGP 3.0 feature - isochronous mode operation - specifically improves graphics operations that require predictable, uninterrupted data flow. Previous versions of the AGP interface cannot guarantee the required bandwidth for latency-sensitive transfers. This “best effort” arrangement works well to achieve low average latency and high average throughput, but does not protect against an occasional arbitrarily long delay now and then, and therefore can result in lost data. Streaming applications—applications that involve real-time flows of digital information for video broadcasts, network downloads, and similar tasks—do not tolerate data loss and require predictable transfers. Further, low-cost designs require a manner to support isochronous transfers without increasing the required amounts of expensive data buffering. With isochronous mode operation, AGP 3.0 addresses these application requirements in a cost-effective manner. Compatibility The AGP 3.0 specification provides a smooth upgrade path to AGP 8X. The mechanical bus specification remains the same. AGP 8X speeds and capabilities are achieved by taking advantage of some previously unused pins, but in a manner that facilitates the support of AGP 8X cards in existing AGP 2X and 4X systems, as well as new systems that fully leverage the 8X interface. NVIDIA AGP 8X graphics solutions will be able to detect the AGP level of the host system, and automatically configure the AGP interface to run in 3.0 mode (at 4X or 8X speeds), or in 2.0 mode (at 2X or 4X speeds). Therefore, a new NVIDIA graphics solution will be fully capable of 8X speeds, and will be completely compatible with 2X, 4X, and 8X systems. The NVIDIA-based cards will automatically deliver the maximum speed supported by the host system. A Note On Names It's a common thing for products to have different naming conventions based on the market that they are sold in. Because of this, the GeForce4 Ti 4600-8X part from NVIDIA was also given the name GeForce4 Ti 4800. In the US, the part, and cards built using it, will use the name GeForce4 Ti 4600-8X; while in other markets, the name GeForce4 Ti 4800 will be used. So, to dispel any possible confusion, its good to know that the GeForce4 Ti 4600-8X is the same as the GeForce4 Ti 4800, and the GeForce4 Ti 4400-8X is the same as the GeForce4 Ti 4800SE. |




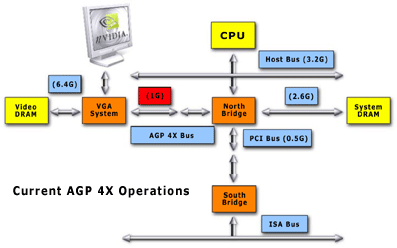 AGP
4X bandwidth falls short of the rest of the system. With AGP 8X, the graphics
bandwidth will be balanced with the other system and memory throughput
rates.
AGP
4X bandwidth falls short of the rest of the system. With AGP 8X, the graphics
bandwidth will be balanced with the other system and memory throughput
rates.